Daily Routine Foods
Dietitian Kabita Maharjan, in a discussion, shares the basic knowledge on carbohydrate, protein, fat and energy and their importance in our daily lives.
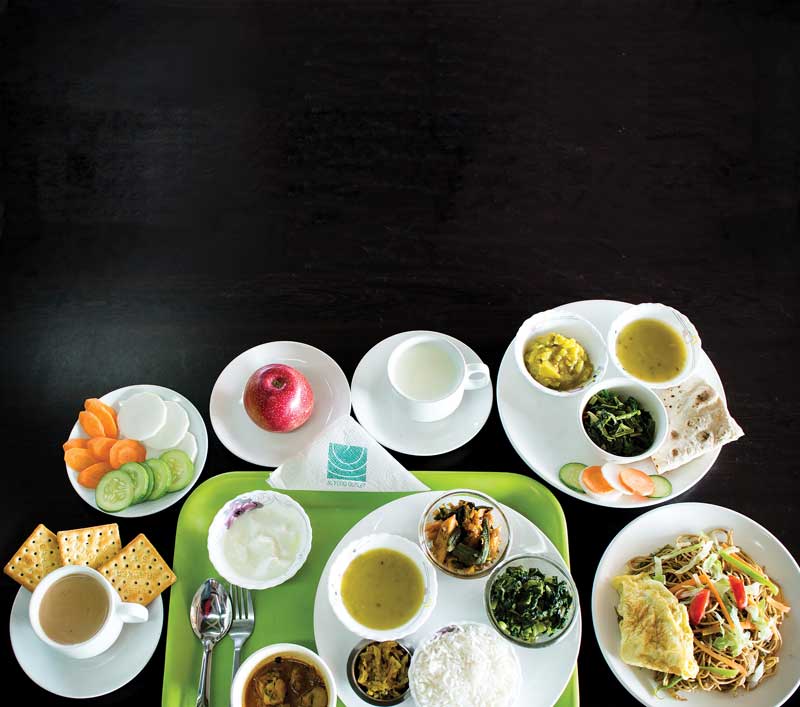

According to dietitian Kabita Maharjan (involved in Nepal Cancer Hospital, Harisiddhi), our body needs a balanced meal consisting of approximately 1600 calories for a day. She has helped in breaking down the food group, and their nutrient value that need to be included in our meals (breakfast, lunch, snacks, and dinner).
Breakfast
1. Milk: starting a day with a glass of milk is giving you Carbohydrate-3, protein-2, fat-2.5, energy-40
2. Biscuit: as per nutritionist, biscuits but with sufficient amount will give you, energy-100
Lunch
1. Rice (white): Each one bowl of serving contain, carb-36, protein-4, energy-160
2. Pulses (Red-gram dal): Only one serving cup of pulses will provide you, carb-13, protein-6, fat-1, energy-80
3. Green leafy vegetables: Many of the root vegetables contain, carb-13, protein-1, fat-5, energy-80
4. Meat: Chicken precisely has protein-9, fat-5, enegy-80
Fruits and salad
For refreshment an apple will boost you up with carb-18, protein-2, energy-80.
Day-break
Noodles: Carb- 36, protein-4, energy-160
Dinner
1. Rice (white): Carb-36, protein-4, energy-160
2. Pulses (Red-gram dal): Carb-13, protein-6, fat-1, energy-80
3. Green leafy vegetables: Carb-13, protein-1, fat-5, energy-80
4. Meat: Protein-9, fat-5, enegy-80
|
S.No |
Food Items |
Nutrients |
|
1 |
Rice, and wheat Bajra, jowar, maize, ragi |
Energy, protein, iron, thiamin, niacin, fiber, energy |
|
2 |
Pulses(dals), legumes |
B complex vitamins, invisible fat, fiber |
|
3 |
A. Green leafy vegetables Spinach, lettuce, etc |
Vitamin C, iron, calcium, folic acid, fiber |
|
|
B. Vitamin C rich vegetables and fruits Amla, guava, papaya, sweet lemon etc |
Vitamin C, carotene, fiber minerals, |
|
|
C. Root and tubers Radish, turnip. |
Vitamin ,iron, mineral, fiber |
|
4 |
Milk and milk products Eggs, meat, fish, poultry |
Protein, energy, calcium, Iron |
|
5 |
Oils, Fats and Sugar Oils, ghee, butter, mayonnaise, sugar |
Energy, fat, essential fatty acid |
The objective of food is not only to provide us energy, but also to provide nutrients which are essential for growth and development, and for maintaining optimal body function.
Good food is one of the basic requirements of human life. As Hippocrates rightly said, “Our food should be our medicine and our medicine should be our food.” The objective of food is not only to provide us energy, but also to provide nutrients which are essential for growth and development, and for maintaining optimal body function. According to many nutritionists’ the most essential macro-nutrients include protein, carbohydrate and fat.
As Goethe said, “Knowing is not enough; we must apply. Willing is not enough; we must do.” It is important to have knowledge about what and where we get the nutrients and calories but what is more important is being able to implement in our lives to make our bodies and minds healthy and strong. Calorie can be said as Kilocalories- Kcal and defined as the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of water by 1 degree Celsius from 14 degree Celsius to 15 degree Celsius. The standard unit for energy measurement is calorie.
Dietary fiber plays an important role on a balanced diet and the major objectives of it are:
• Meets nutritional requirement
• Prevents degenerative diseases
• Improves longevity
• Improves immunity
• Increases endurance level
• Develops optimum cognitive ability
There are five food groups, as shown in the table below, and each food items in the food groups have different nutrient in them. With the help of this table planning your meals could be easier and heathier.