Understanding nutrition journey
Anjali Goyal, a renowned nutritionist, offers practical advice on healthy eating. She provides tips on meal planning, shopping lists, and batch cooking. Goyal also shares strategies for nutritious snacks, quick meals, mindful eating, healthier takeout opt
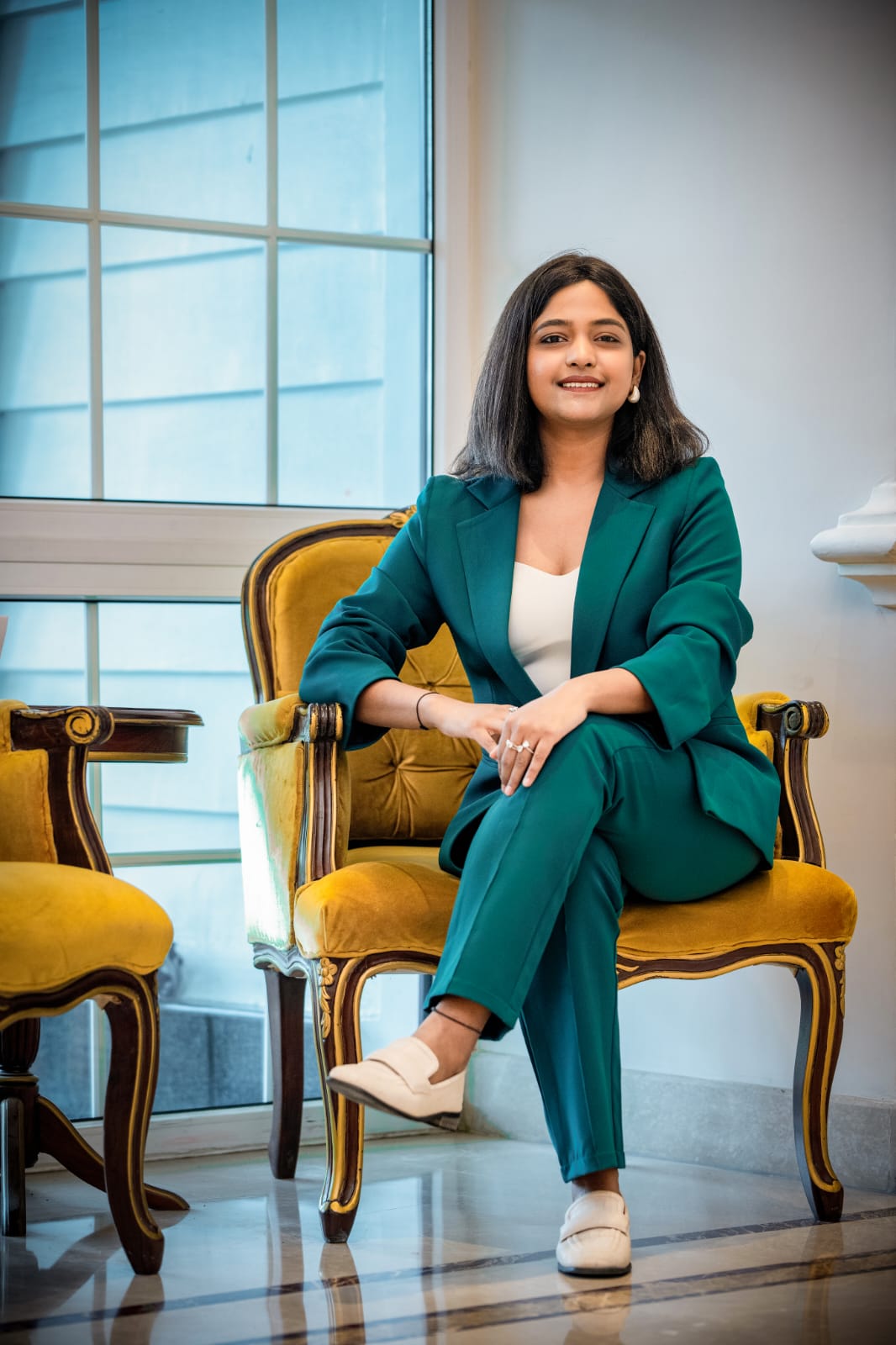

Who is Anjali Goyal and what inspired you to become a clinical and sports nutrition consultant?
Anjali Goel, a clinical and sports nutrition consultant, offers personalized nutrition services to Nepalese and the Nepalese diaspora worldwide. Her brand, Nutrimantra, focuses on creating customized nutrition plans tailored to individual health goals and lifestyle habits, using ingredients and cuisine from the Nepali Kitchen. With six years of experience, Goel has helped many clients lose weight, reverse medical vitals, and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Goel believes nutrition and health should be approachable and not an expensive hobby. She has a deep-rooted belief in the power of nutrition to transform lives and is dedicated to living a balanced and healthy life. Her journey into clinical and sports nutrition was driven by personal passion and a desire to make a tangible impact on people's lives. Her sports and fitness experiences and academic pursuits have fuelled her passion for nutrition and the power of nutrition to transform lives.
What are some common misconceptions about nutrition that you encounter in your practice?
1. Carbs Are the Enemy:
In reality, carbohydrates are a crucial energy source, especially for athletes. The key is to choose complex carbs, like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, over simple,
refined ones.
2. Fat Makes You Fat:
However, healthy fats, such as those found in cheese, nuts, and olive oil, are essential for various bodily functions, including hormone production and nutrient absorption. Moderation and the type of fat consumed are what matter.
3. Supplements Can Replace a Healthy Diet:
While supplements can be beneficial in certain situations, they should not replace a balanced diet. Whole foods provide a complex array of nutrients that supplements cannot fully replicate.
4. "You Have to Eat 'Clean' All the Time":
The idea that you must always eat perfectly to be healthy is unrealistic and can lead to unhealthy relationships with food. Balance and moderation are more sustainable and effective for long-term health.
5. "Eating Late at Night Causes Weight Gain":
Weight gain is more about what and how much you eat rather than when you eat. It's the total daily calorie intake and expenditure that matter most.
6. "Skipping Meals Helps You Lose Weight":
Skipping meals can lead to overeating later and can negatively impact metabolism. Regular, balanced meals help maintain energy levels and support a healthy metabolism.
Some tips for maintaining a balanced diet while managing a busy lifestyle?
• Weekly meal planning and shopping list creation.
• Batch cooking and meal prepping to save time and reduce unhealthy choices.
• Stocking pantry, desk, and car with healthy snacks like nuts, fruits, yogurt, and whole grain crackers.
• Choosing quick, nutritious meals like stir-fries, salads, grain bowls, channa chiura, anda chuira.
• Mindful eating to improve digestion and recognize fullness.
• Opting for healthier takeout options like salads, grilled proteins, and vegetable sides.
• Be mindful of portion sizes, especially when eating out, to avoid overeating.
How can individuals identify and address their unique nutritional needs?
1. Consult a Registered Dietitian: A registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide personalized advice and meal plans.
2. Assess Current Diet: A food diary can identify nutritional gaps or patterns.
3. Understand Body's Signals: Pay attention to how different foods make you feel.
4. Consider Health Conditions: Tailor dietary approaches for specific health conditions like diabetes, hypertension, allergies, or digestive disorders.
5. Look at Lifestyle Factors: Physical activity, work schedule, sleep patterns, and stress levels affect nutritional needs.
6. Genetic Testing and Biomarkers: These tests can identify specific nutritional needs or sensitivities.
7. Educate Yourself: Understand the basics of nutrition, including macronutrients and micronutrients.
8. Set Realistic Goals: Define what you want to achieve with your nutrition.
9. Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review your diet and make adjustments as needed.
10. Stay Hydrated: Ensure adequate water intake daily and adjust intake based on activity level, climate, and individual needs.
What are your thoughts on popular diet trends, such as keto, intermittent fasting, and plant-based diets?
Keto Diet
• High in fats and low in carbohydrates, can lead to weight loss and improved blood sugar control.
• Beneficial for individuals with certain neurological conditions.
• Can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not managed well.
• May cause negative side effects like "keto flu," digestive issues, and increased cholesterol levels.
• Requires guidance from a healthcare professional for nutritional balance.
Intermittent Fasting:
• Promotes weight loss, improves metabolic health, and enhances longevity.
• Flexible with various methods like the 16/8 method, 5:2 diet, or alternate-day fasting.
• May not be suitable for everyone, especially those with a history of eating disorders, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and certain medical conditions.
• Effective if aligned with lifestyle and dietary preferences.
Plant-Based Diets:
• Rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
• Can lead to improved heart health, lower risk of chronic diseases, and a smaller environmental footprint.
• Can lead to potential nutrient deficiencies and social and cultural challenges.
• Can be highly nutritious when well-planned.
• Consultation with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended for tailored diets.
As our new regular writer on nutrition, what topics can our readers look forward to learning about from you in future issues?
1. Balancing macronutrients and understanding micronutrients.
2. Healthy eating on a budget.
3. Incorporating Nepali cuisines.
4. Efficient meal planning and prep tips.
5. Benefits of plant-based diets.
6. Debunking common nutrition myths.
7. The role of gut health in overall wellness.
8. Eating for mental health.
9. Special dietary needs guidance.
10. Sustainable eating practices.
11. Nutrition across different life stages.
12. The science and use of supplements.
13. Mindful eating practices.
14. Evaluating nutrition trends and fads.
15. Personalized nutrition based on individual needs.